Solr token matching
Docs and sources:
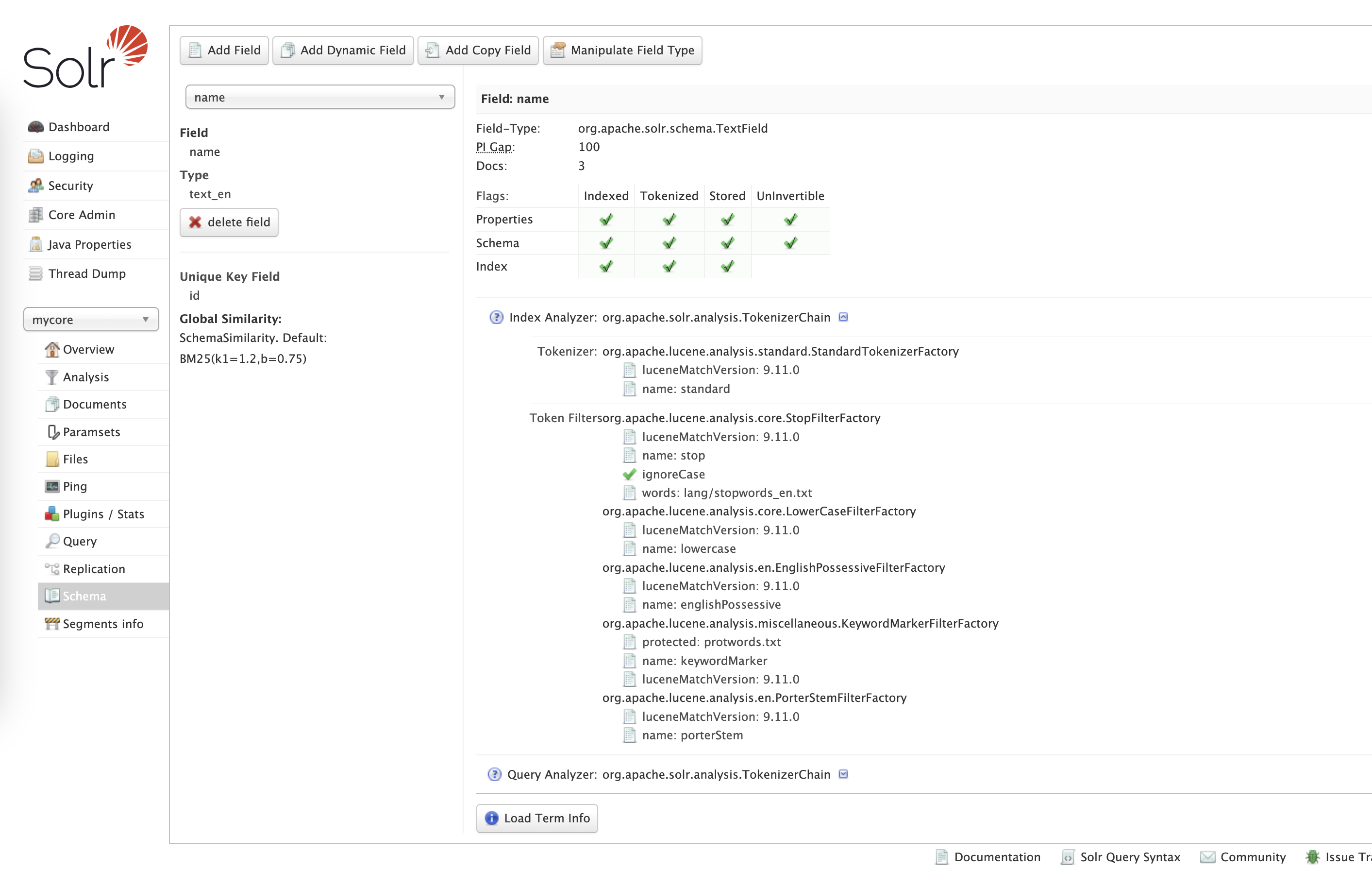
How do Solr performs token matching?
Let's assume we have defined the field name as type text_en from the default managed-schema.xml file in the Solr
distribution: managed-schema.xml
This fieldType is defined like this:
<fieldType name="text_en" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizer name="standard"/>
<!-- in this example, we will only use synonyms at query time
<filter name="synonymGraph" synonyms="index_synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/>
<filter name="flattenGraph"/>
-->
<!-- Case insensitive stop word removal.
-->
<filter name="stop"
ignoreCase="true"
words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"
/>
<filter name="lowercase"/>
<filter name="englishPossessive"/>
<filter name="keywordMarker" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<!-- Optionally you may want to use this less aggressive stemmer instead of PorterStemFilterFactory:
<filter name="englishMinimalStem"/>
-->
<filter name="porterStem"/>
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizer name="standard"/>
<filter name="synonymGraph" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/>
<filter name="stop"
ignoreCase="true"
words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"
/>
<filter name="lowercase"/>
<filter name="englishPossessive"/>
<filter name="keywordMarker" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<!-- Optionally you may want to use this less aggressive stemmer instead of PorterStemFilterFactory:
<filter name="englishMinimalStem"/>
-->
<filter name="porterStem"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
Indexing pipelines
So it has the following index-time analyzers:
- tokenizer
standard- splits the phrase into tokens by whitespace and punctuation - filter
stop- removes stopwords defined inlang/stopwords_en.txt - filter
lowercase- makes all tokens lowercase - filter
englishPossessive- removes'sfrom words - filter
keywordMarker- protects words (defined inprotowords.txt) from being modified by further stemmers - filter
porterStem- stemmer, changes the word into it's basic form
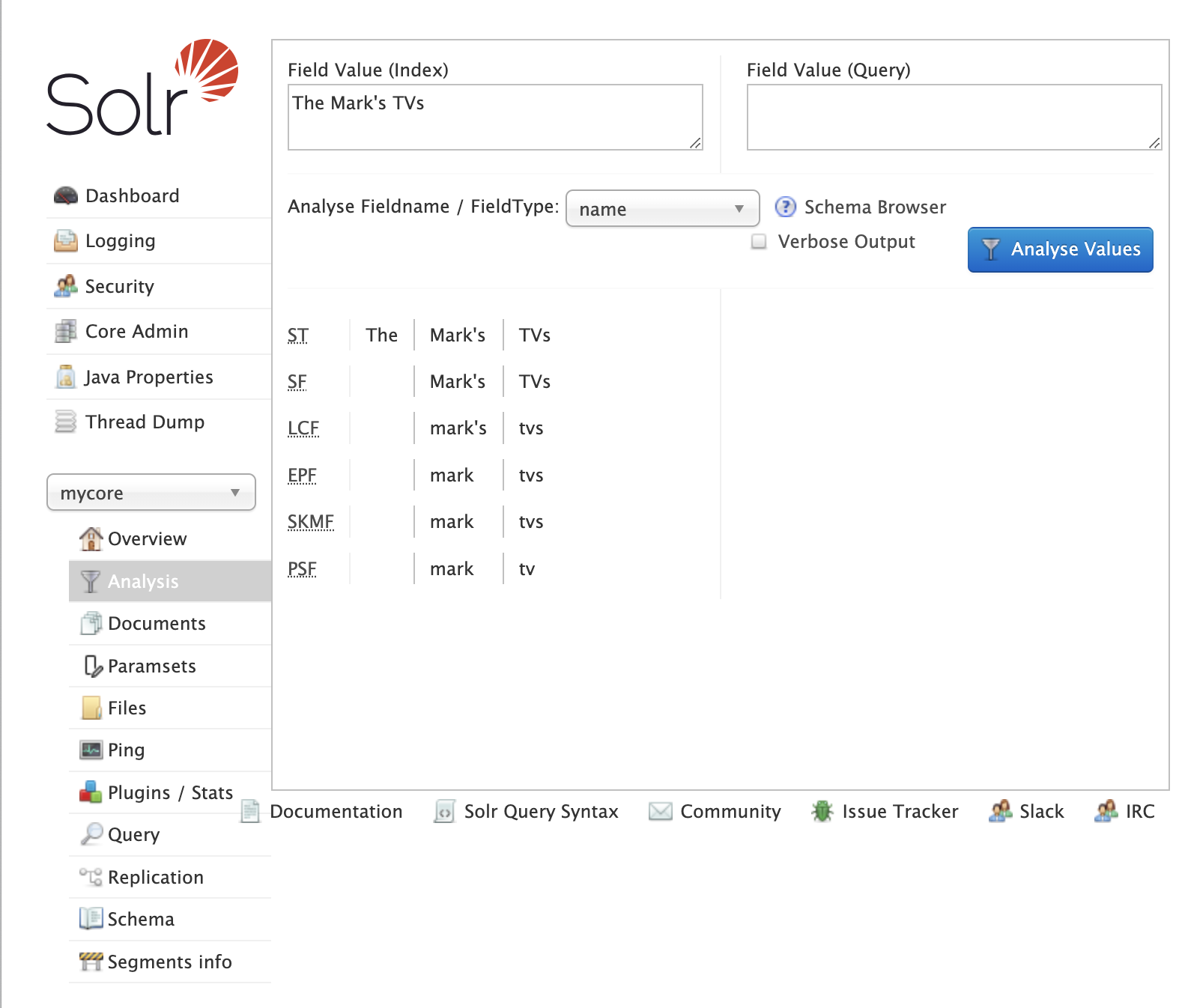
On every document update, the field's value is passed by the indexing pipeline to create tokens. We can simulate this process in the Solr's UI
This is rather self-explanatory.
- Standard Tokenizes splits the phrase into tokens by whitespace and punctuation
- Stopword filter removes the stopword
The - Lowercase filter makes it all lowercase
- English Possessive changes
mark'sintomark - Keyword Marker does nothing in this case (but we could use it to protect f.ex. "tvs" from further processing)
- Stemmer changes words to its stems, here
tvsintotv
Query pipeline
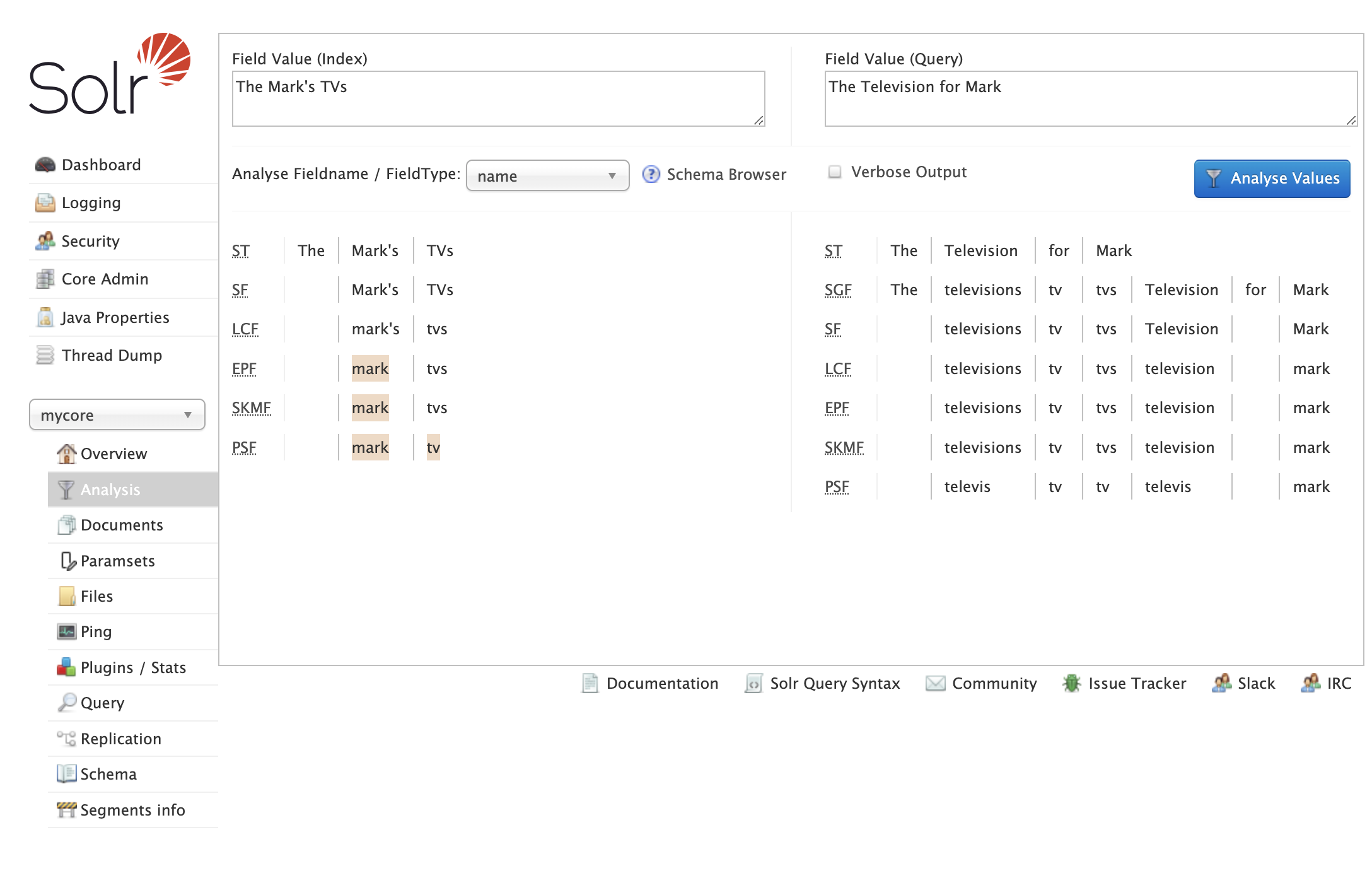
The query-time analyzers defined for this field are similar, except that
we have an additional filter: synonymGraph with synonyms defined in synonyms.txt file
Every search query is split into tokens by query-time analyzers. So let's check what will happen if we enter some query:
- Tokenizer splits the query into tokens
- Synonyms filter creates synonyms for
TV - Lowercase filter makes it all lowercase
- English Possessive checks for
's(there are no words like this in the query) - Keyword Marker does nothing in this case
- Stemmer changes words to its stems, here
tvsintotv,televisionintotelevis
We have matching tokens here
The UI shows also that tokens mark and tv are a match between query token and indexed token - matching tokens are highlighted.
But watch out!
On the token level, the match must be exact - car would not match cars. You need to define the appropriate
analyzers to make sure that different grammatical forms will be handled correctly.
Notworthy: stems might not be existing words
In this example the stem from television is televis.
This is fine, stems are the most basic form which is shared between all grammatical variants of the word,
but stem itself does not need to form a valid word by its own.
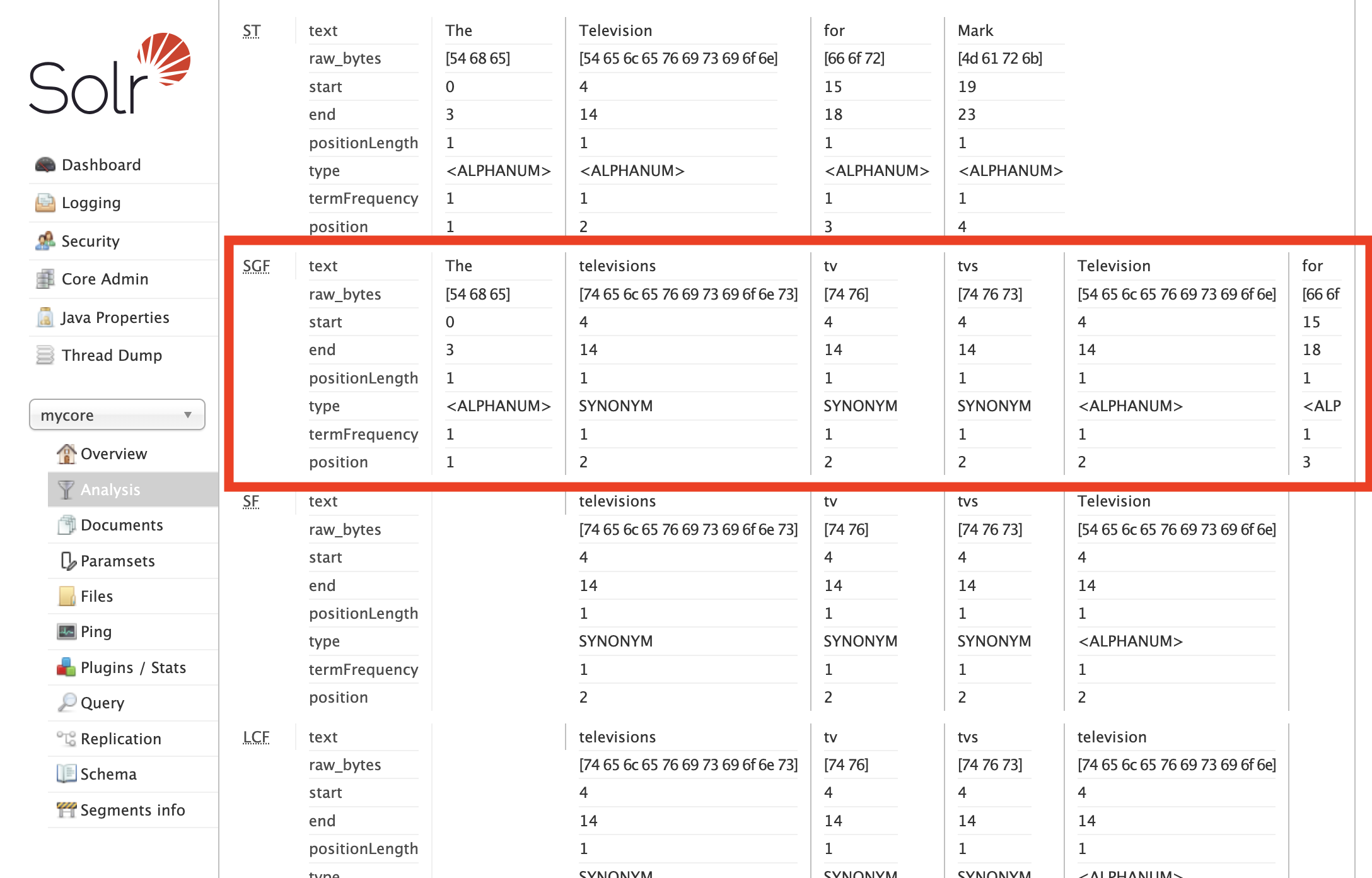
Why do we have synonyms multiplied?
On a non-verbose output we can be surprised that we have four synonyms instead of a single word.
However, if we enable verbose output and scroll down, we can see more details:
We can see that all synonyms:
- have the same
startandend - has the same
position - are of type
SYNONYM
This all means that Solr knows, that these are alternative tokens placed in the same position.